Science behind use of antenatal corticosteroids, CPAP and surfactant
- Introduction...
- 1. What shall we l...
- 2. Quantum of prem...
- 3. Vulnerability i...
- 4. How do antenata...
- 5. What is CPAP?...
- 6. What does CPAP ...
- 7. PVR increases a...
- 8. CPAP and Surfac...
- 9. Surfactant prod...
- 10. What did we le...
 |
 |
Introduction
Dr. SUSHMA NANGIA
MD, DM (Neonatology)
Director Professor & Head
Department of Neonatology
LHMC & Kalawati Saran Children’s Hospital, New Delhi
1. What shall we learn?
► How do Antenatal Steroids (ANS) work?
► How does CPAP work?
► How does surfactant work?
► Synergistic action of ANS, CPAP and surfactant
2. Quantum of prematurity
India has the
♦ Highest number of preterm births and
♦ Highest number of neonatal deaths due to prematurity
► Births - 2.6 crore live births/ year
► Preterm births - 35 lakh/ year
► Preterm deaths - 3 lakh babies (10%)
3. Vulnerability in prematurity
► Fetal lung immaturity - principal contributor for neonatal
mortality
► Primary focus of strategies to improve the survival - lung
► Strategy for prevention and treatment of RDS
♦ Acceleration of fetal lung maturation by ANS therapy to the
mother
♦ CPAP to the neonate
♦ Surfactant to neonate
4. How do antenatal steroids work?
► Accelerates development of pneumocytes, improve lung
mechanics (maximal lung volume, compliance), gas exchange
► Increases surfactant production
► Induction of surfactant release, absorption of alveolar fluid,
increases lung antioxidant enzymes
► Reduction in RDS, reduction in intraventricular hemorrhage,
necrotizing enterocolitis, mortality, systemic sepsis and
mortality
5. What is CPAP?
CPAP – Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
Application of continuous pressure during
both inspiration and expiration in a
spontaneously breathing baby
6. What does CPAP do?
►Provides constant airway pressure
♦ Keeps the alveoli open
♦ Keeps airways splinted & open (improves FRC)
► Leads to
♦ Better breathing
♦ Better gas exchange – Less lung injury
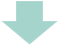
7. PVR increases at lung volumes below and above FRC
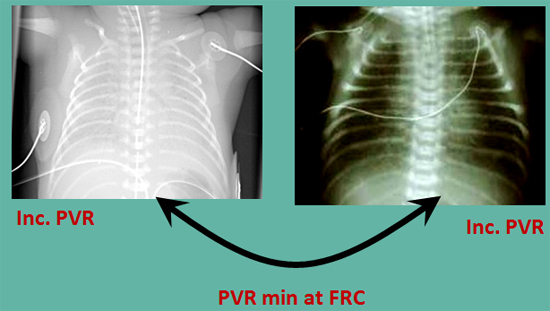
8. CPAP and Surfactant Together!
9. Surfactant production
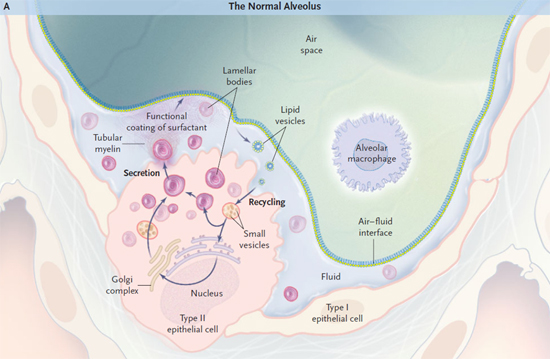
10. What did we learn?
► CPAP is safe as it causes less lung injury
► Give optimal CPAP to open the lung at FRC as PVR is least
with maximum blood flow
► Surfactant and CPAP together is beneficial in RDS
► CPAP will give maximum dividends if used with antenatal
steroids and early surfactant when required
► Good delivery room care and use early CPAP
► Acceptance by team
