Classification and severe forms of ROP
- Introduction...
- 1. Learning object...
- 2. Classification ...
- 3. Location...
- 4. Severity...
- 6. Plus disease...
- 7. Aggressive Post...
- 8. Consequences of...
- 9. Key messages...
- 5. Severity - 01...
 |
 |
Introduction
DR. J. KUMUTHA
MD, DCH
Professor & Head
Department of Neonatology
Saveetha Medical College
Thandalam, Chennai
1. Learning objectives
► To learn about the
♦ classification of ROP
♦ severe forms of ROP
♦ consequences of ROP
2. Classification of ROP
► International Classification of ROP (ICROP) is used for
classifying ROP
► ROP is categorised based on
♦ the severity into stages (1-5)
♦ location into 3 zones (Zone 1-3)
♦ the presence of plus disease
3. Location


4. Severity
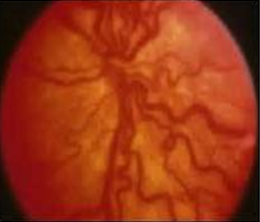
6. Plus disease
► Increased venous dilation
► Arteriolar tortuosity of the posterior retinal vessels
► If there is poor pupillary dilatation (rigid pupil), you should
suspect plus disease
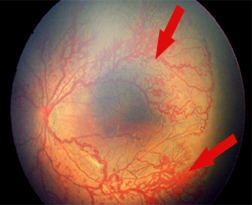
7. Aggressive Posterior ROP (AP-ROP)
► Rapidly progressing, severe form of ROP in the smallest
and most immature infants
► Prominence of plus disease
► There is risk of early retinal detachment
8. Consequences of ROP
► Refractive errors
► Squint
► Unilateral or bilateral blindness
► Late retinal detachment (6 months-31 years)
► Glaucoma
9. Key messages
► ROP is classified based on the severity, location and extent
of the disease
► The presence of plus disease and APROP needs urgent
intervention in the form of laser or surgery
► Screening and timely intervention will reduce dire
consequences of ROP
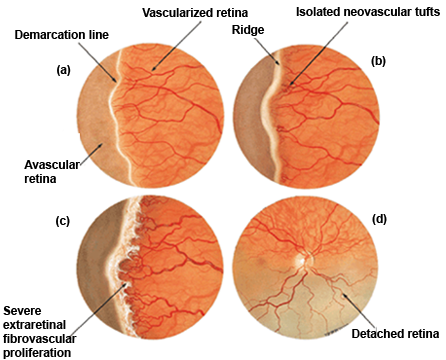
5. Severity - 01
► Stage 1 - Thin white line of demarcation's
► Stage 2 - Addition of depth and width to the demarcation line
(Ridge)
► Stage 3 - Presence of extra retinal fibro vascular proliferation
► Stage 4 - Partial retinal detachment beginning at the ridge,
not involving macula (4A) and involving macula (4B)
► Stage 5 - Complete retinal detachment
