Screening and follow up of ROP
- Introduction...
- 1. Learning object...
- 2. Whom to screen?...
- 3. When to screen?...
- 4. ROP screening: ...
- 5. Preparation of ...
- 7. Planning follow...
- 8. Linking with RB...
- 9. Key messages...
- 6. Preparation of ...
 |
 |
Introduction
DR. AMANPREET SETHI
MD, DM (Neonatology)
Assistant Professor
Department of Pediatrics
All India Institute of Medical Sciences
New Delhi
1. Learning objectives
► Whom to screen?
► When to screen?
► Who will screen?
► How to prepare a baby for screening?
► How to plan follow up?
2. Whom to screen?
Infants with either of the following
♦ Birth weight less than 2000 grams OR
♦ Gestation age less than 35 weeks OR
Any preterm infant with following risk factors
♦ Cardio-respiratory instability
♦ Prolonged oxygen therapy
♦ Repeated episodes of apnea of prematurity
♦ Blood transfusion
♦ Sepsis
♦ Poor postnatal weight gain
3. When to screen?
► First screening at 4 weeks of age
► For infants between 24-30 weeks GA /Birth weight < 1200
gram: 2-3 weeks after delivery (Not later than 3 weeks)
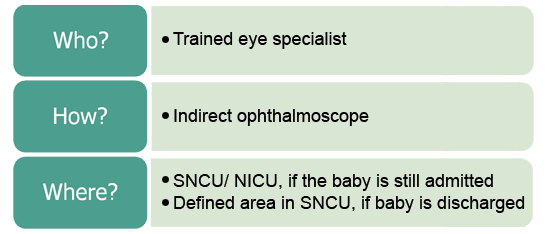
4. ROP screening: Place, person and equipment
5. Preparation of babies prior to screening

7. Planning follow up interval

8. Linking with RBSK
► Improve coordination and financial support
► Provision of equipment to screen and treat
► Long term follow up can be streamlined by involvement
of front line health workers
► Improvement of rehabilitation/referral services
9. Key messages
► ROP screening should be done at 4 weeks after birth
► Infants born earlier than 30 weeks/ birth weight <1200
grams: do examination at 2-3 weeks
► The screening should be done by trained
ophthalmologists using indirect ophthalmoscope
► The frequency of follow up depends upon the zone and
stage of ROP
6. Preparation of babies prior to screening 2

