CPAP Maintenance and monitoring
- Introduction...
- 1. Maintenance and...
- 2. CPAP and FiO
- 3. CPAP...
- 4. Warming and hum...
- 5. Humidifier...
- 6. Monitoring...
- 7. Chest X-ray...
- 8. Adequacy of CPA...
- 9. Weaning...
- 10. Procedure afte...
- 11. Failure of CPA...
- 12. Reasons for fa...
- 13. Summary...
 |
 |
Introduction
DR. SRINIVAS MURKI
MD, DM (Neonatology)
Consultant Neonatologist
Fernandez Hospital
Hyderguda, Hyderabad
1. Maintenance and monitoring
► Flow
♦ Bubble minimal bubbling (2 to 7 liters/min)
♦ Ventilator 6 to 8 cms of water
► FiO2 (21% to 60 %) : SpO2 90% - 95%
► CPAP (4 to 7 cms) : Recessions/ CXR and SpO2
2. CPAP and FiO2: Proportionality
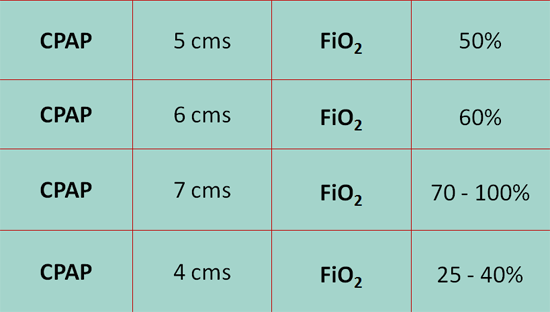
3. CPAP
► CPAP of < 4 cm H2O never given
► CPAP of 4-7 cm H2O is a good range
♦ Advantages many, disadvantages few!
► CPAP of > 7 cm H2O is a bad range
♦ Advantages some, disadvantages galore!
4. Warming and humidification
► Temperature of inspiratory gases at 37o C
► Relative humidity of 100%
► No condensation in the inspiratory circuit
► Some condensation in the expiratory limb
5. Humidifier

6. Monitoring
► Patient
♦ HR, RR, SAS score, SpO2, air entry and bubbling
♦ CFT, blood pressure, anterior fontannel, urine output,
abdominal girth
► Machine
♦ CPAP pressure, FiO2 and flow
♦ Water in humidifier, bubble chamber
♦ Condensation in circuit
► Interface
♦ Nasal injury, cap size, prong size, secretions
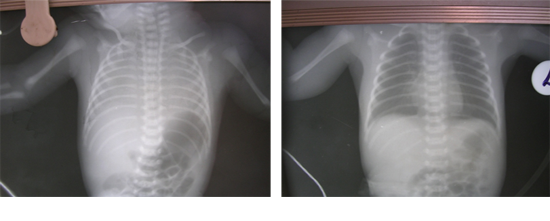
7. Chest X-ray
8. Adequacy of CPAP
► Satisfactory cardiorespiratory status
♦ Comfortable baby
♦ Minimal retraction, no grunt
♦ Normal capillary refill, BP
♦ Normal saturations: 90 - 94%
♦ Normal ABG
(PaO2: 60-80, PaCO2: 40-60, pH 7.35-7.45, BE±2)

9. Weaning
► Decrease FiO2 and then CPAP
► Every 1 cm decrease in CPAP, aim 10% in FiO2
► CPAP 5cm & FiO2 50%, maintain CPAP till FiO2 is 30%
► Decrease CPAP to 4 cm
► The disease process has improved
► Remove CPAP, if CPAP 4 cm & FiO2 < 30% & clinically well
(no RD, SpO2 > 90% & normal ABG)
10. Procedure after the CPAP
► Oral and nasal suction/ saline nebulization, if secretions
► Watch for apneas, tachypnea, retractions and bradycardia
► Frequent change in positions
11. Failure of CPAP
► Continuing retractions, grunt
► Recurrent apneas
► SpO2 <90 % & PaO2 < 50 : PEEP > 7 & FiO2 >60%
► PaCO2 > 55, poor respiratory efforts
► Baby not tolerating CPAP
12. Reasons for failure
► Failure of the CPAP system
► Worsening of baby
♦ Respiratory
♦ Cardiovascular
♦ Neurological
13. Summary
► Titration
♦ Flow Bubbling
♦ FiO2 SpO2
♦ CPAP Recessions/CXR
► Proportionality of FiO2 and CPAP
► Systematic evaluation: Failure of CPAP
